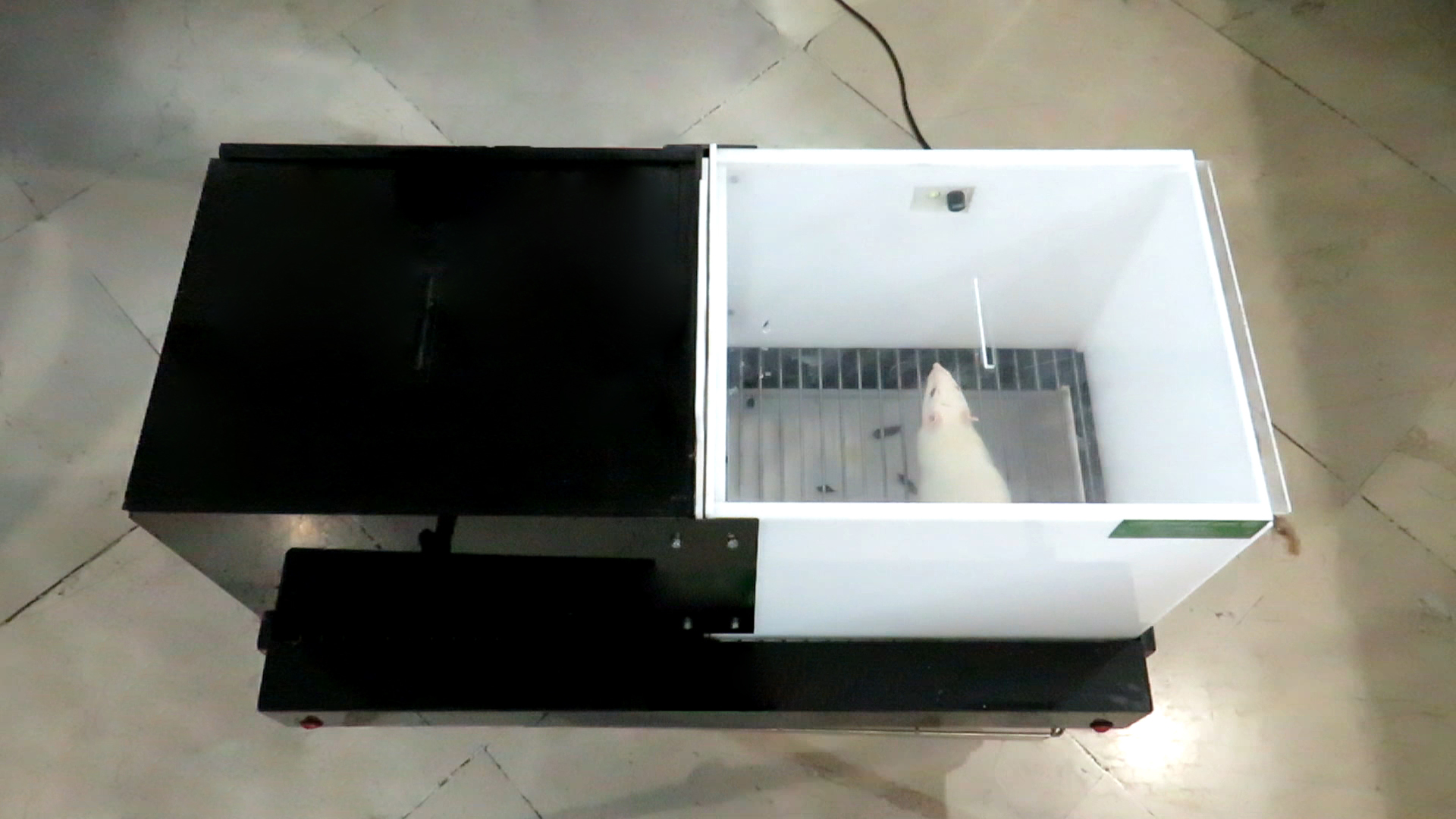
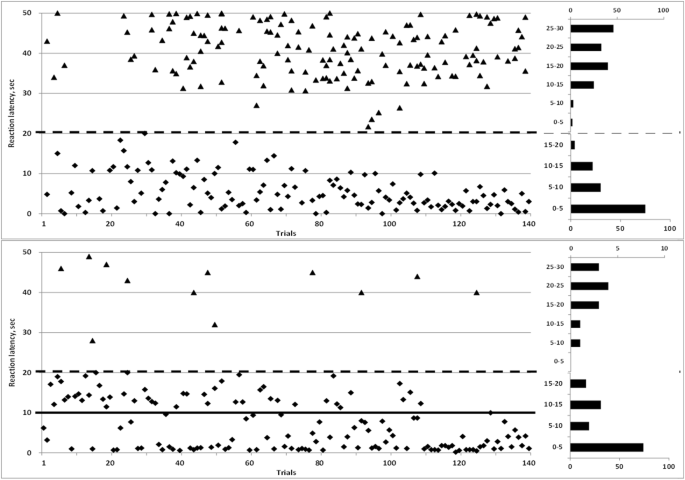
An active avoidance behavioral paradigm for use in a mild closed head model of traumatic brain injury in mice - ScienceDirect

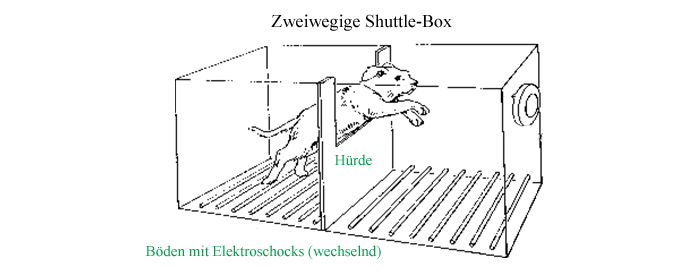
The shuttle box apparatus and tasks. Apparatus: the shuttle box (940 mm... | Download Scientific Diagram

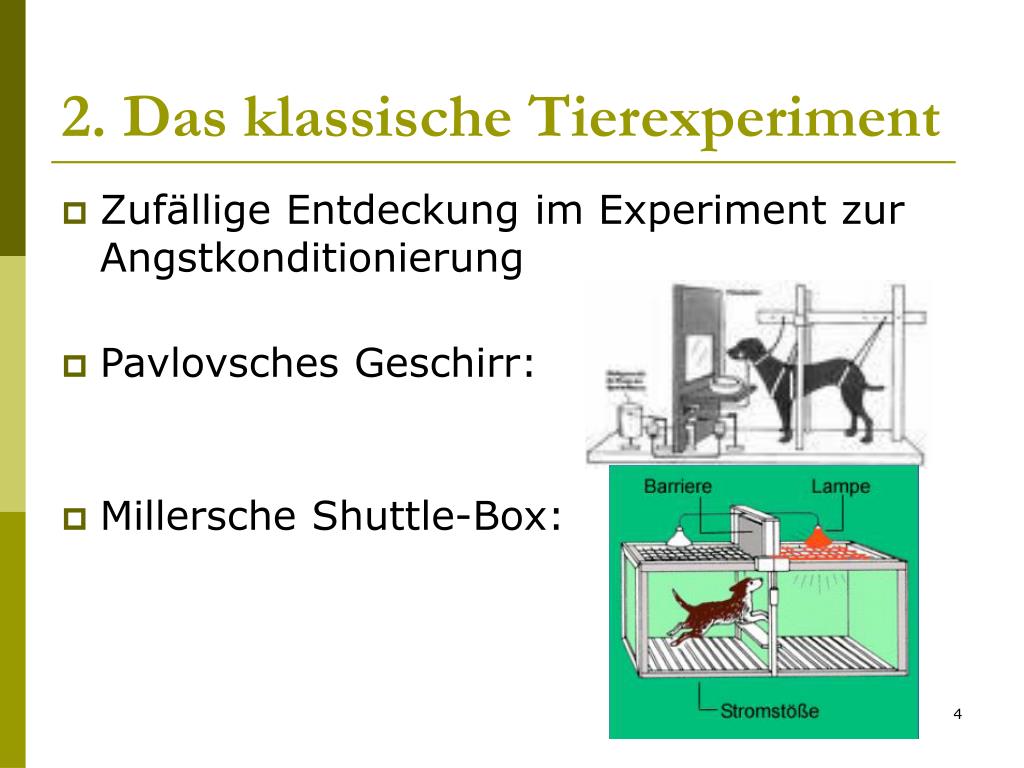
An active avoidance behavioral paradigm for use in a mild closed head model of traumatic brain injury in mice - ScienceDirect
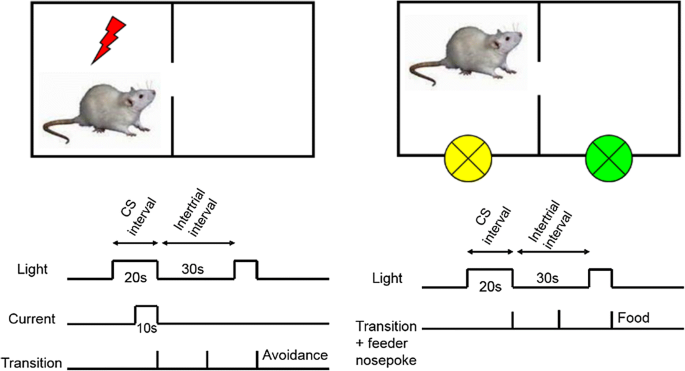
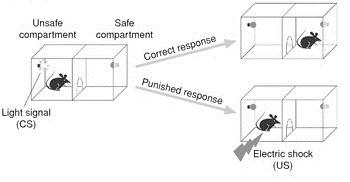
Appetitive conditioning task in a shuttle box and its comparison with the active avoidance paradigm | SpringerLink

Experimental setup. (A) Snapshot of a gerbil in the shuttle-box. (B)... | Download Scientific Diagram